Understanding Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannoma)
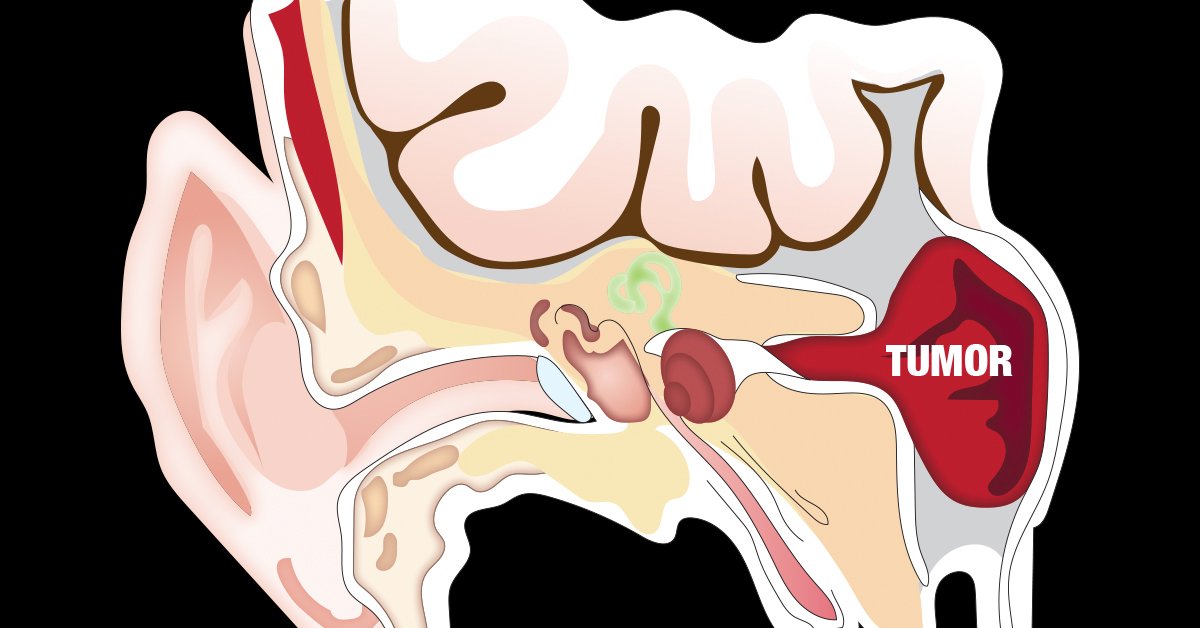
An Acoustic Neuroma, also known as a Vestibular Schwannoma, is a benign tumor that develops on the vestibulocochlear nerve, responsible for hearing and balance. Though slow-growing, it can press on surrounding nerves and brain structures, affecting hearing, balance, and facial function.
Common Symptoms of Acoustic Neuroma
Symptoms develop gradually and may include:
- Gradual or sudden hearing loss, usually in one ear
- Ringing in the ear (tinnitus)
- Balance problems or unsteadiness
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Facial numbness, weakness, or tingling
- Headaches in larger tumors due to pressure on brain structures
Diagnosis
Diagnosis includes a detailed neurological and audiological evaluation. Key investigations are:
- MRI with contrast: Identifies tumor size, location, and relation to nerves and brainstem
- CT scan: Helpful in some cases for bone involvement
- Audiometry: Hearing tests to assess cochlear function
- Balance assessments: Evaluate vestibular function
Treatment Options
Treatment is tailored based on tumor size, symptoms, and patient health:
- Microsurgical Removal: Safe excision with neuronavigation and intraoperative monitoring
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (Gamma Knife / CyberKnife): Non-invasive radiation for small or residual tumors
- Observation (“Wait and Watch”): Periodic MRI for small, asymptomatic tumors
- Rehabilitation: Balance and hearing therapy post-treatment
Expert Care in Ahmedabad
At HCG Aastha Cancer Centre, Ahmedabad, Dr. Chirag Panchal offers advanced management of Acoustic Neuromas using microneurosurgery, neuroendoscopy, and intraoperative neuromonitoring. His approach prioritizes preservation of facial and hearing functions while achieving effective tumor control.
Recovery & Follow-up
- Regular monitoring of hearing, balance, and facial nerve function
- Periodic MRI scans to detect recurrence
- Early intervention ensures optimal long-term outcomes
When to Seek Medical Help
- Hearing loss in one ear
- Persistent tinnitus or ringing in the ear
- Balance or coordination problems
- Facial weakness or numbness


