Understanding Hemifacial Spasm
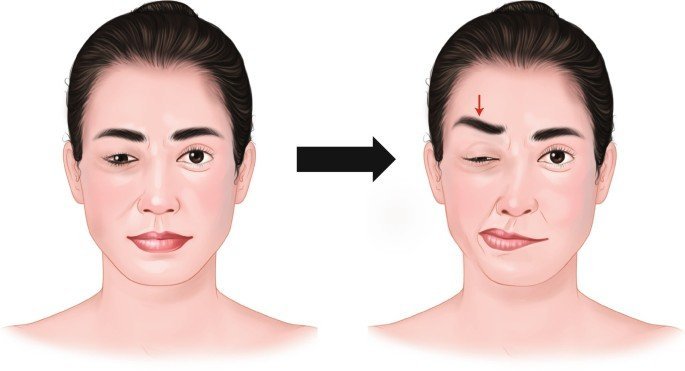
Hemifacial spasm is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary, intermittent muscle contractions on one side of the face. These spasms usually start around the eye and can spread to the cheek, mouth, and neck.
Hemifacial spasm typically affects adults and is more common in middle-aged and older individuals. It can be caused by blood vessels compressing the facial nerve, tumors, or facial nerve injury.
Common Symptoms of Hemifacial Spasm
- Involuntary twitching or contractions on one side of the face
- Gradual worsening of spasms over time
- Involuntary eye closure
- Asymmetrical facial expressions
- Rarely, difficulty speaking or eating if severe
Causes and Risk Factors
Hemifacial spasm usually occurs due to compression of the facial nerve by a blood vessel at its root exit zone from the brainstem. Other causes include facial nerve injury, tumors, or certain neurological conditions.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves neurological evaluation and imaging studies:
- MRI / MRA: Detects vascular compression, tumors, or other structural causes.
- Neurological Examination: Assesses muscle function and nerve involvement.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures electrical activity of facial muscles.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on severity and underlying cause:
- Botulinum Toxin Injections: Temporarily paralyze muscles to relieve spasms—most common first-line therapy.
- Microvascular Decompression Surgery: Relieves nerve compression by repositioning the blood vessel—permanent solution for eligible patients.
- Medications: Rarely, anticonvulsants or muscle relaxants may be used if surgery or injections are not suitable.
Advanced Hemifacial Spasm Care in Ahmedabad
At HCG Aastha Cancer Centre, Ahmedabad, Dr. Chirag Panchal, Consultant Neurosurgeon, offers expert evaluation and treatment of hemifacial spasm using advanced microvascular decompression techniques, Botox therapy, and comprehensive neurological care to ensure symptom relief and improved quality of life.
When to Seek Medical Help
- Persistent or worsening facial spasms
- Spasms affecting vision or eye closure
- Difficulty speaking, eating, or facial movement
- Sudden changes in facial nerve function
Early evaluation and treatment of hemifacial spasm help prevent complications and improve day-to-day functioning.


